What is Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. Specific applications of AI include expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition and machine vision.
How does AI work?
As the hype around AI has accelerated, vendors have been scrambling to promote how their products and services use AI. Often what they refer to as AI is simply one component of AI, such as machine learning. AI requires a foundation of specialized hardware and software for writing and training machine learning algorithms. No one programming language is synonymous with AI, but a few, including Python, R and Java, are popular.
In general, AI systems work by ingesting large amounts of labeled training data, analyzing the data for correlations and patterns, and using these patterns to make predictions about future states. In this way, a chatbot that is fed examples of text chats can learn to produce lifelike exchanges with people, or an image recognition tool can learn to identify and describe objects in images by reviewing millions of examples.
AI programming focuses on three cognitive skills: learning, reasoning and self-correction.
Learning processes. This aspect of AI programming focuses on acquiring data and creating rules for how to turn the data into actionable information. The rules, which are called algorithms, provide computing devices with step-by-step instructions for how to complete a specific task.
Reasoning processes. This aspect of AI programming focuses on choosing the right algorithm to reach a desired outcome.
Self-correction processes. This aspect of AI programming is designed to continually fine-tune algorithms and ensure they provide the most accurate results possible.
Why is artificial intelligence important?
AI is important because it can give enterprises insights into their operations that they may not have been aware of previously and because, in some cases, AI can perform tasks better than humans. Particularly when it comes to repetitive, detail-oriented tasks like analyzing large numbers of legal documents to ensure relevant fields are filled in properly, AI tools often complete jobs quickly and with relatively few errors.
This has helped fuel an explosion in efficiency and opened the door to entirely new business opportunities for some larger enterprises. Prior to the current wave of AI, it would have been hard to imagine using computer software to connect riders to taxis, but today Uber has become one of the largest companies in the world by doing just that. It utilizes sophisticated machine learning algorithms to predict when people are likely to need rides in certain areas, which helps proactively get drivers on the road before they’re needed. As another example, Google has become one of the largest players for a range of online services by using machine learning to understand how people use their services and then improving them. In 2017, the company’s CEO, Sundar Pichai, pronounced that Google would operate as an “AI first” company.
Today’s largest and most successful enterprises have used AI to improve their operations and gain advantage on their competitors.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of artificial intelligence?
Artificial neural networks and deep learning artificial intelligence technologies are quickly evolving, primarily because AI processes large amounts of data much faster and makes predictions more accurately than humanly possible.
While the huge volume of data being created on a daily basis would bury a human researcher, AI applications that use machine learning can take that data and quickly turn it into actionable information. As of this writing, the primary disadvantage of using AI is that it is expensive to process the large amounts of data that AI programming requires.
Advantages
- Good at detail-oriented jobs;
- Reduced time for data-heavy tasks;
- Delivers consistent results; and
- AI-powered virtual agents are always available.
Disadvantages
- Expensive;
- Requires deep technical expertise;
- Limited supply of qualified workers to build AI tools;
- Only knows what it’s been shown; and
- Lack of ability to generalize from one task to another.
Strong AI vs. weak AI
AI can be categorized as either weak or strong.
- Weak AI, also known as narrow AI, is an AI system that is designed and trained to complete a specific task. Industrial robots and virtual personal assistants, such as Apple’s Siri, use weak AI.
- Strong AI, also known as artificial general intelligence (AGI), describes programming that can replicate the cognitive abilities of the human brain. When presented with an unfamiliar task, a strong AI system can use fuzzy logic to apply knowledge from one domain to another and find a solution autonomously. In theory, a strong AI program should be able to pass both a Turing Test and the Chinese room test.
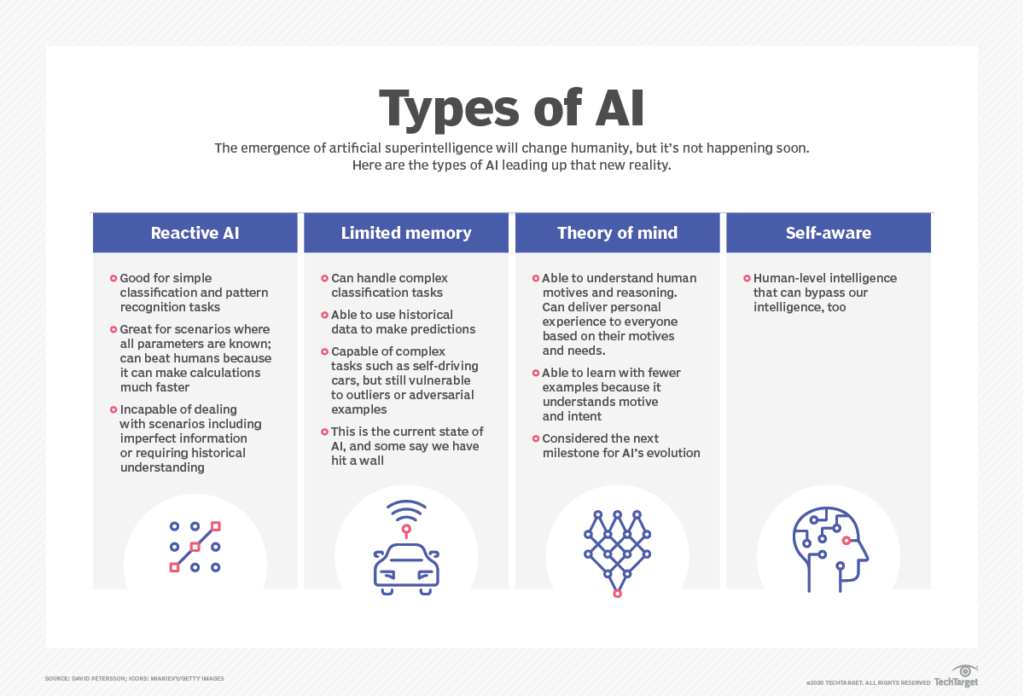
What are the 4 types of artificial intelligence?
Arend Hintze, an assistant professor of integrative biology and computer science and engineering at Michigan State University, explained in a 2016 article that AI can be categorized into four types, beginning with the task-specific intelligent systems in wide use today and progressing to sentient systems, which do not yet exist. The categories are as follows:
- Type 1: Reactive machines. These AI systems have no memory and are task specific. An example is Deep Blue, the IBM chess program that beat Garry Kasparov in the 1990s. Deep Blue can identify pieces on the chessboard and make predictions, but because it has no memory, it cannot use past experiences to inform future ones.
- Type 2: Limited memory. These AI systems have memory, so they can use past experiences to inform future decisions. Some of the decision-making functions in self-driving cars are designed this way.
- Type 3: Theory of mind. Theory of mind is a psychology term. When applied to AI, it means that the system would have the social intelligence to understand emotions. This type of AI will be able to infer human intentions and predict behavior, a necessary skill for AI systems to become integral members of human teams.
- Type 4: Self-awareness. In this category, AI systems have a sense of self, which gives them consciousness. Machines with self-awareness understand their own current state. This type of AI does not yet exist.
The publication of this article, by Ed Burns, Nicole Laskowski, Linda Tucci, has been extracted and freely adapted from TechTarget.com

